Our furry friends bring joy and companionship, but they can also face various skin issues. Understanding these conditions helps in maintaining your dog’s health and comfort. Here are ten common skin conditions in dogs, their symptoms, causes, and ways to address them.
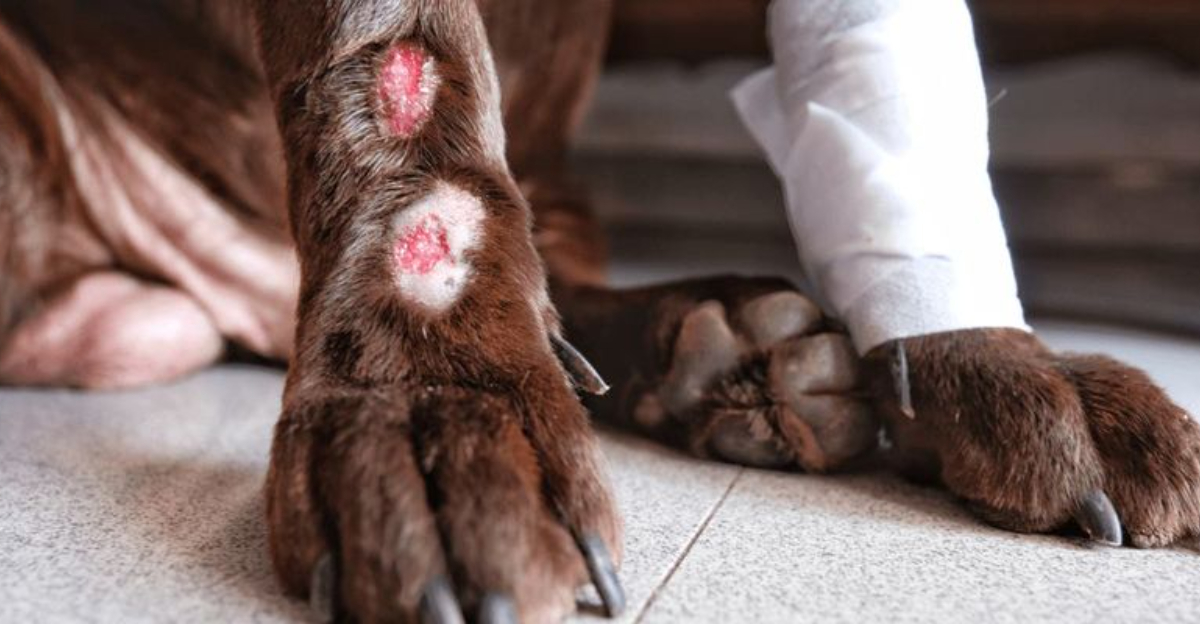
Hot Spots
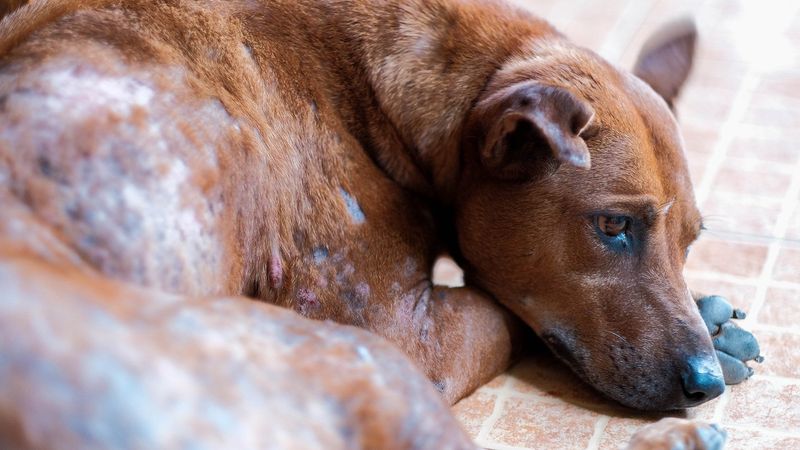
Hot spots, or acute moist dermatitis, appear as red, inflamed areas on a dog’s skin. These can develop rapidly and may ooze or crust over. Dogs often lick or scratch these areas excessively, exacerbating the condition. Hot spots are commonly caused by bites, allergies, or poor grooming.
Keeping your dog’s coat clean and dry, along with regular grooming, can help prevent hot spots. Treating underlying causes, like allergies or parasites, is essential. If your dog suffers from hot spots, a vet visit may be necessary to prevent infection and alleviate discomfort.
Allergic Dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis in dogs leads to itchy, irritated skin, often accompanied by redness or rashes. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, and certain foods. Dogs may react with intense scratching, biting, or rubbing against surfaces.
Identifying the allergen is crucial in managing this condition. Allergy tests or elimination diets may be necessary. Treatments include antihistamines, special shampoos, or dietary changes. Regular cleaning of your dog’s environment can reduce allergen exposure, offering relief and a happier pup.
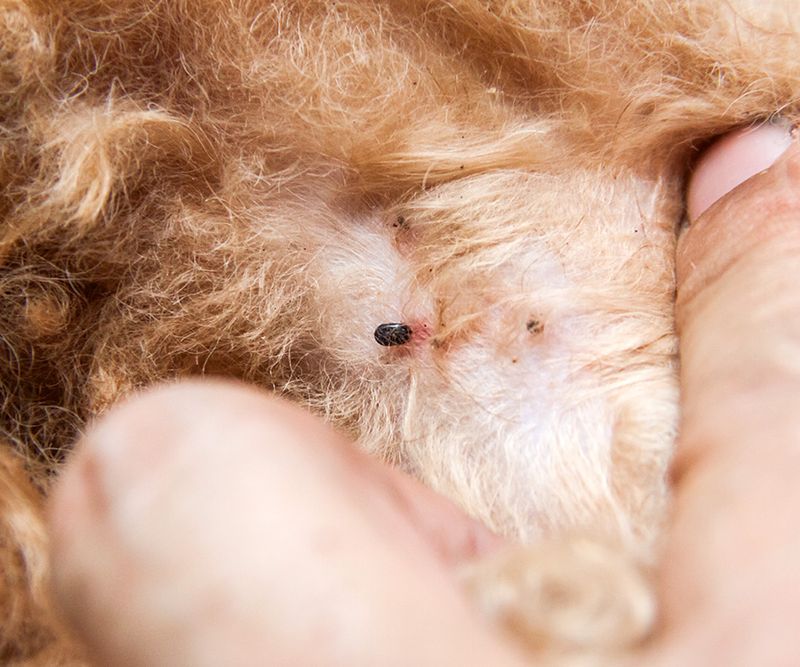
Flea Allergy Dermatitis
Flea allergy dermatitis is a common issue where dogs react strongly to flea saliva. A single flea bite can lead to intense itching, hair loss, and irritated skin. Dogs may bite or scratch affected areas, primarily around the tail or hindquarters.
To manage flea allergy dermatitis, consistent flea control is vital. Using flea preventatives year-round and keeping the environment clean helps. In severe cases, a vet may prescribe medication to alleviate itching and heal the skin.
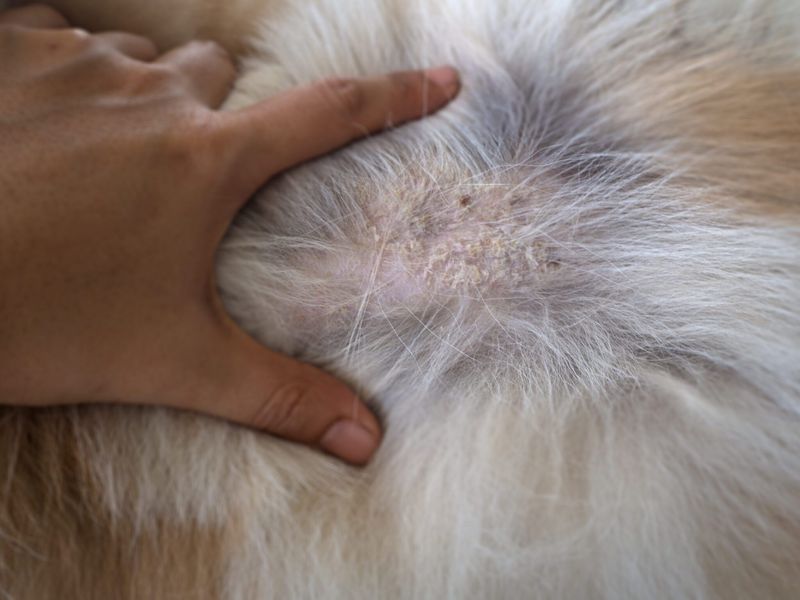
Ringworm
Ringworm is a contagious fungal infection that affects a dog’s skin, presenting as circular patches of hair loss with red, scaly skin. Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm but by fungi known as dermatophytes.
Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent spread. Antifungal medications or shampoos can effectively treat ringworm. Isolating affected pets and maintaining hygiene prevents transmission to other animals or humans. Regularly cleaning bedding and grooming tools is also recommended.
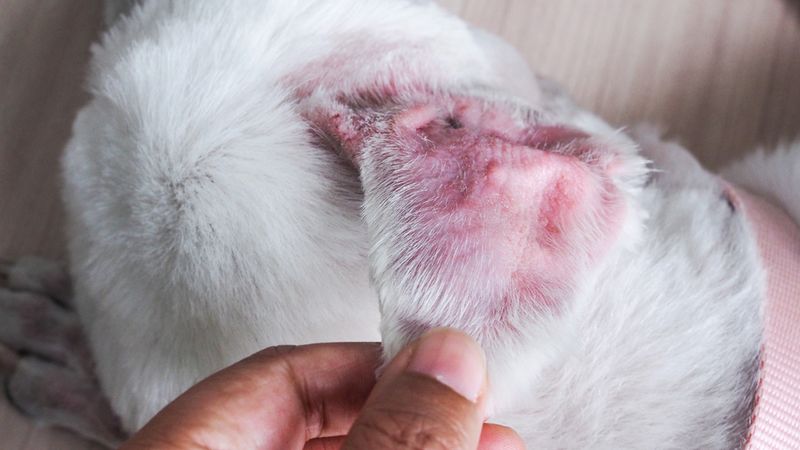
Yeast Infections
Yeast infections in dogs often occur in moist areas, like the ears, paws, or folds of the skin. Symptoms include greasy, smelly skin, redness, and itching. Factors such as allergies or a weakened immune system can increase susceptibility.
Regular cleaning and drying of affected areas help prevent yeast infections. Antifungal treatments from a vet can address existing infections. Ensuring your dog’s diet supports a healthy immune system also aids in preventing recurrences.
Seborrhea
Seborrhea results in oily, flaky skin in dogs. It can be a primary condition or secondary to other issues like allergies or hormonal imbalances. Symptoms include dandruff, greasy skin, and a strong odor.
Managing seborrhea involves regular bathing with medicated shampoos to reduce flakiness and oiliness. Identifying and treating any underlying causes is essential for effective management. A balanced diet and supplements like omega-3 fatty acids can also improve skin health.
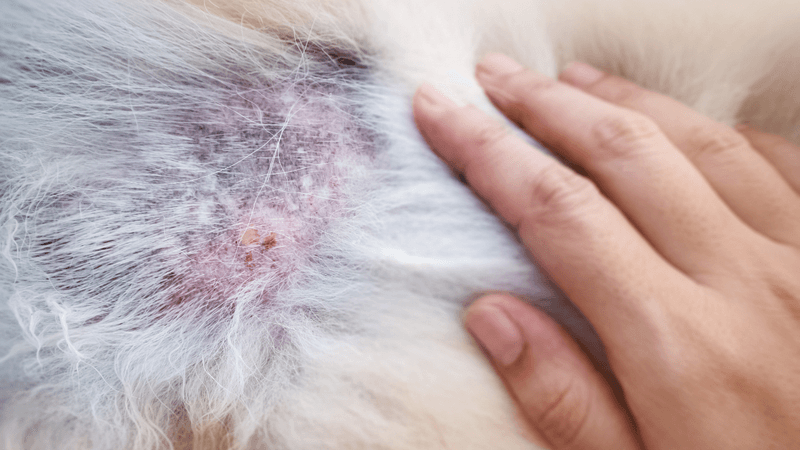
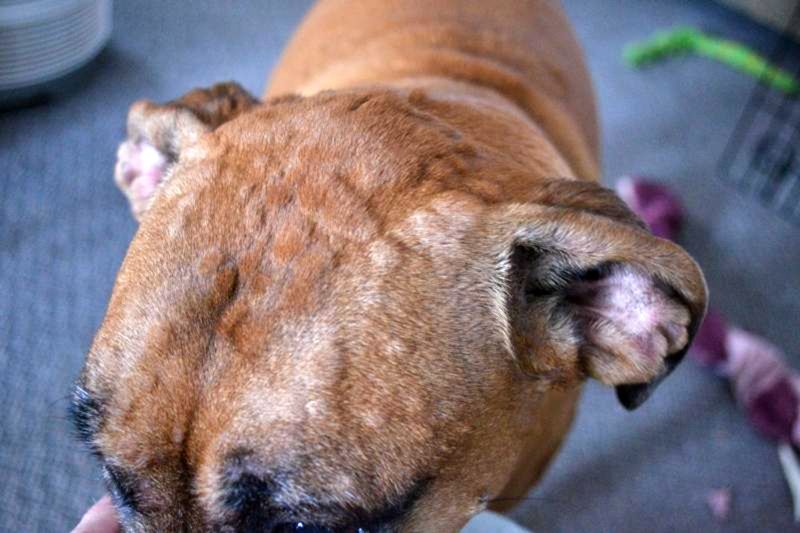
Mange
Mange is caused by mites that lead to intense itching and hair loss in dogs. There are two types: demodectic and sarcoptic, each with distinct symptoms and treatments. Mange can cause severe discomfort and skin infections.
Veterinary diagnosis is necessary to determine the type of mange and appropriate treatment. Medications to kill mites and soothe the skin are available. Preventing mange involves maintaining good hygiene and regular veterinary check-ups.
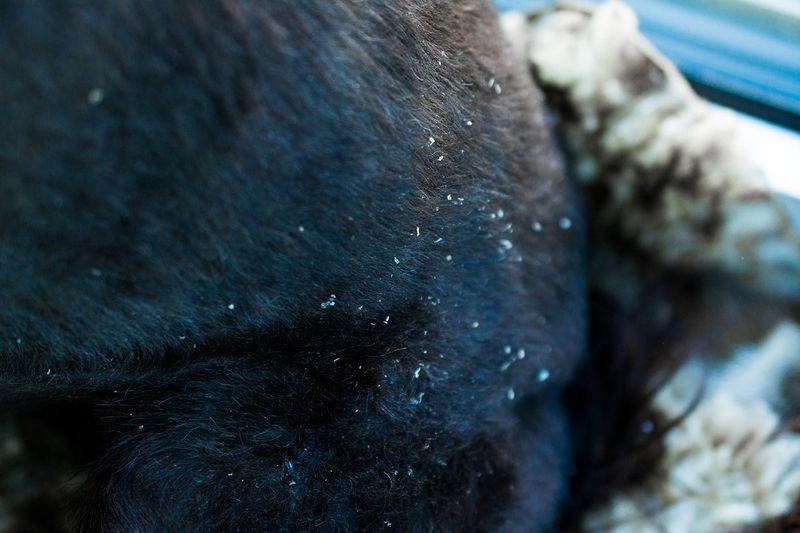
Dandruff
Dog dandruff presents as white flakes in the fur, often accompanied by dry, itchy skin. It can be caused by poor diet, lack of grooming, or underlying health issues.
Improving your dog’s diet, ensuring proper hydration, and regular grooming can alleviate dandruff. Special shampoos may also be recommended to moisturize the skin and reduce flakes. If dandruff persists, a vet visit is advised to rule out other conditions.
Hives
Hives in dogs appear as raised, itchy welts on the skin, often triggered by allergies, insect bites, or environmental factors. They appear suddenly and can be alarming but are typically not serious.
Identifying and avoiding the trigger is key to managing hives. Antihistamines can be administered to reduce itching and swelling. Most hives resolve quickly without treatment, but persistent or severe cases should be evaluated by a vet.
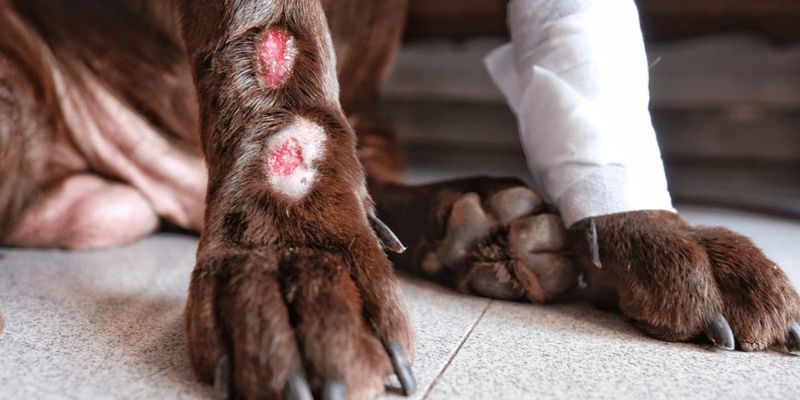
Lick Granuloma
Lick granuloma occurs when a dog obsessively licks an area, usually on the legs, creating a raw, inflamed sore. Causes include boredom, anxiety, or underlying skin conditions. The cycle of licking and inflammation perpetuates the problem.
Breaking the cycle involves addressing the root cause, whether behavioral or medical. Treatment options include behavior modification, topical medications, or even protective coverings. Consulting a vet ensures a comprehensive approach to healing and preventing future occurrences.